![ultrafast laser chiller ultrafast laser chiller]()
As technology becomes advanced and more and more new kinds of materials are invented, components are becoming lighter, smaller and more precise. The requirement of material processing in different areas is also more and more demanding years after years. In this kind of condition, traditional processing methods can no longer meet the new processing requirement and they seem to gradually fade out. And long pulsed laser, EDM and other processing can not realize the consistency between design and actual processing effect because of the heat affecting zone. So any kind of method is qualified in the pursuit of precision manufacturing? Well, ultrafast laser is no doubt one of the candidates.
Ultrafast laser has extremely narrow pulse width, very high energy density and very short interaction time with the material, so it becomes the most ideal tool in precision manufacturing. Comparing with traditional processing methods, ultrafast laser is easier to operate, more flexible and more eco-friendly with higher quality. This has greatly expanded the application and the potential of the precision manufacturing, making it applicable in automobile, medical, aerospace, new materials and so on.
The common ultrafast laser includes femtosecond laser, picosecond laser and nanosecond laser. So why ultrafast laser outperforms traditional laser in material manufacturing?
Traditional laser uses hot stack from the laser energy so that the interacted area of the material will melt or even evaporate. In this process, drawbacks like a great amount of crumbs, micro-crack will appear. And the longer the interaction, the more damage the traditional laser will cause to the material. But ultrafast laser is quite different. The interaction time is quite short and the energy from the single pulse is strong enough to cause ionization to any material so that the processing purpose can be achieved. That means ultrafast laser has the advantages of ultrahigh precision and very low damage that traditional long pulsed lasers don't have. Meanwhile, ultrafast laser is more applicable, for it can be used on metal, TBC coating, composite material and other non-metal materials.
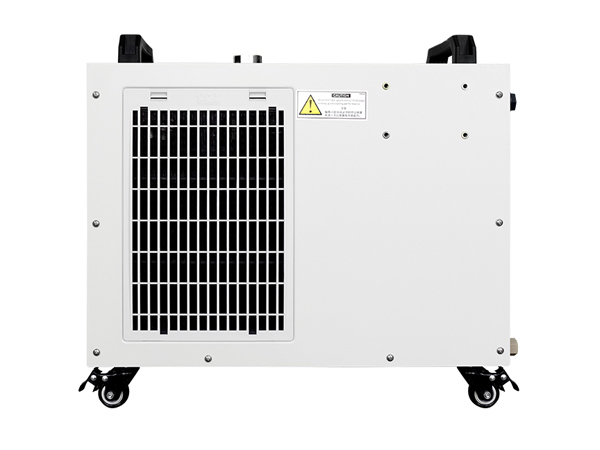
Ultrafast laser and high precision laser chiller often come hand in hand. The more precise the water chiller, the more stable performance of the ultrafast laser will be achieved. This means the selection of water chiller is quite demanding. So any kind of high precision laser chiller recommended? Well, S&A Teyu small laser water chiller CWUP-20 is ideal candidate. This high precision laser chiller is able to deliver continuous cooling with ±0.1℃ stability for ultrafast laser up to 20W. Modbus-485 communication protocol is supported in this chiller so that the communication between the laser and the chiller can be very easy. This chiller also comes with an easy-fill port and easy-drain port together with an easy-to-read level check. This kind of user-friendly design has won a dozen of ultrafast lasers from many countries in the world. For more information of this small laser water chiller, click https://www.teyuchiller.com/portable-water-chiller-cwup-20-for-ultrafast-laser-and-uv-laser_ul5
![ultrafast laser chiller ultrafast laser chiller]()