Industrial CO2 laser is also called glass laser tube and it is a kind of laser source with relatively high continuous output power. It is widely applied to textile, medical, material processing, industrial manufacturing and other areas.
CO2 laser technique became pretty mature in 1980s. The wavelength of the current CO2 laser is 10.64μm and the output light is infrared light. The electro-optical conversion efficiency of CO2 laser can normally reach 15% to 25%, which is better than that of YAG laser. The wavelength of CO2 laser decides the fact that it can be absorbed by may different kinds of non-metal materials.
As the most mature and most reliable and stable laser source, CO2 laser still has the widest applications in Europe, the United States and many different countries. The light beam quality decides the fact that it still has great potential in different applications. Now we are going to name a few.
Surface treatment
In terms of surface treatment of CO2 laser, we mainly refer to laser cladding. Nowadays, we can use laser diode to replace it. But before the advent of high power laser diode, CO2 laser was the major laser source for laser cladding. Laser cladding technique is widely used in mold, hardware, mining machinery, aerospace, marine equipment and other industries. Comparing with laser diode, CO2 laser has a great advantage in price, so it is still the most popular laser source in laser cladding.
Textile processing
In metal fabrication, CO2 laser faces the challenges from fiber laser and laser diode. Therefore, the future application trend for CO2 laser would be non-metal materials. Among the non-metal materials, textile would be one of the most commonly seen. CO2 laser can perform different cutting and engraving forms in the textile, making the textiles more beautiful and personalized. And plus, the market of textile is huge in the first place, so CO2 laser is sure to experience a huge demand in the long run.
Medical application
In the 1990s, CO2 laser was introduced into the cosmetics industry. And as the laser technique becomes more and more advanced, it will attract more and more people.
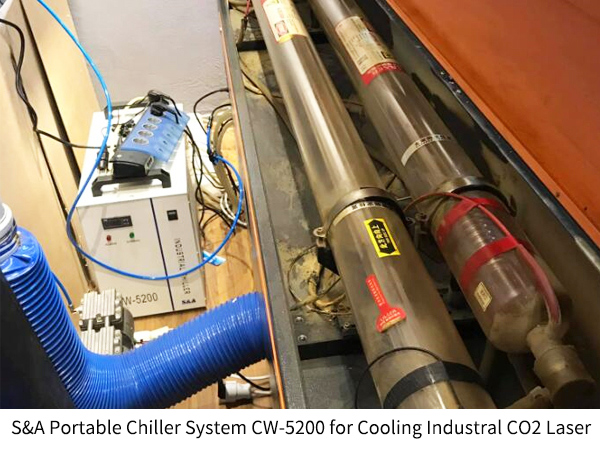
CO2 laser uses CO2 which is a kind of gas as the medium, which easily makes the laser output unstable. Besides, the inner component inside the CO2 laser is very sensitive to thermal changes. Therefore, high precision cooling can make the CO2 laser last longer and make the laser output stable.
S&A Teyu portable chiller system CW-5200 is a reliable high precision cooling system for CO2 laser. It features ±0.3°C temperature stability and the refrigeration capacity of 1400W. Besides, it goes with an intelligent temperature controller which is easy to use and allows automatic water temperature control. Therefore, users can focus on their cutting work and let the cw 5200 chiller do the cooling job quietly.
Find out more information of this chiller model at https://www.teyuchiller.com/recirculating-compressor-water-chillers-cw-5200_p8.html